-
[C언어] ARP 패킷 스니핑 프로그램Coding/개발 2020. 3. 9. 04:00
이번 방학 프로젝트를 통해 발전된 나의 실력을 포스팅 하려고 한다!!!! (음하하핫)
[ 플랫폼 : 리눅스 / 개발언어 : C언어 ]
ARP
[ Address Resolution Protocal ]
어떤 장치의 IP주소를 이용하여 MAC주소를 얻는데 사용하는 프로토콜
Q. ARP 프로토콜이 왜 필요한가?
: LAN(근거리 통신망)상에서 통신을 할때 MAC 주소를 기반으로 통신을 한다.
이때 MAC주소를 알기 위해서 필요한 것!
(LAN 의 표준안 : 물리계층과 데이터링크계층을 표준으로 삼음)
> 더 좋은 의견이 있다면 댓글로 알려주세요!!
ARP 헤더
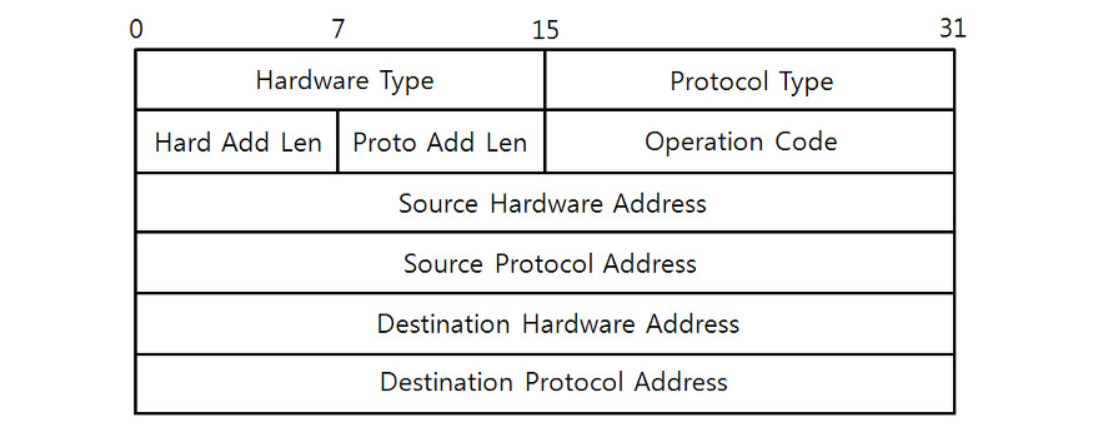
ARP 헤더 그림 [ 구성 ]
하드웨어타입 : 2 byte
프로토콜 타입 : 2byte
하드웨어 주소 길이 : 1byte
프로토콜 주소 길이 : 1byte
OPcode : 2byte
출발지 MAC 주소 : 6byte
출발지 IP 주소 : 4byte
도착지 MAC 주소 : 6byte
도착지 IP 주소 : 4byte
총 42byte ( 이더넷 + ARP 헤더 )
* 헤더 선언 *
struct arp_header { unsigned short Hardw_type; unsigned short Prtoc_type; unsigned char Hardwadd_len; unsigned char Prtocadd_len; unsigned short Op_code; struct ether_addr Arpsed_mac; struct in_addr Arpsed_ip; struct ether_addr Arptar_mac; struct in_addr Arptar_ip; }; // 헤더 선언 성공!!
pcap 함수 정리
pcap_findalldevs(&alldevs, errbuf) : 네트워크 이더넷들을 찾아주는 함수
( alldevs에 찾은 이더넷 정보 저장 / 에러시 errbuf에 에러 저장)
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs) : 해당 네트워크를 제외한 다른 네트워크를 해제하기 위한 함수
pcap_open_live(name, 65536, 1, 1000, errbuf ) : 실제 네트워크 이더넷의 패킷을 캡처 하는 함수
( 장치이름 , 패킷의 길이 , 모든 패킷을 잡을 수 있는 promisc모드로 설정 , 패킷을 읽는 시간 , 에러버퍼 )
pcap_next_ex(adhandle, &header, &pkt_data) : 캡처된 패킷의 데이터를 불러오는 함수
* 코드 *
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <pcap.h> struct ether_addr { unsigned char mac_add[6]; }; struct ether_header { struct ether_addr etherdst_mac; struct ether_addr ethersed_mac; unsigned short ether_type; // ARP인지 확인 할 수 있는 부분 0x0806=ARP 0x0800=IP // short=2byte }; #pragma pack(push, 2) // 구조체 크기 정렬하기 = 2바이트 단위로 메모리 낭비없이 저장하기 위함. struct arp_header { unsigned short Hardw_type; unsigned short Prtoc_type; unsigned char Hardwadd_len; unsigned char Prtocadd_len; unsigned short Op_code; // 패킷의 유형(req인지 rep인지 정의/req=1/rep=2) struct ether_addr Arpsed_mac; struct in_addr Arpsed_ip; struct ether_addr Arptar_mac; struct in_addr Arptar_ip; }; #pragma pack(pop) void print_ether_header(const unsigned char *pkt_data); void print_arp_header(const unsigned char *pkt_data); int main() { pcap_if_t *alldevs; // 포인터 alldevs의 자료형은 pcap_if_t pcap_if_t *d; int inum,res,i=0; struct pcap_pkthdr *header; //pcap_pkthdr 구조체 : const unsigned char *pkt_data; //패킷을 저장할 공간 pcap_t *adhandle; char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; char packet_filter[] = ""; // 사용자가 원하는 프로토콜 필터 정보를 넣을 수 있는 공간 struct bpf_program fcode; // 특정 프로토콜만을 캡쳐하기 위한 정책정보 저장 if(pcap_findalldevs(&alldevs, errbuf) == -1) { // alldevs 에 디바이스 목록 저장,에러시 errbuf에 에러저장 printf("Error in pcap_findalldevs: %s\n", errbuf); exit(1); } for(d=alldevs; d; d=d->next) { //네트워트 디바이스 정보를 출력 printf("%d. %s", ++i, d->name); if (d->description) printf(" (%s)\n", d->description); else printf(" (No description available)\n"); } if(i==0) { //디바이스 못찾을 경우 에러 printf("\nNo interfaces found! Make sure LiPcap is installed.\n"); //return -1; } printf("Enter the interface number (1-%d):",i); scanf("%d", &inum); if(inum < 1 || inum > i) { //입력한 값이 올바른지 판단 && : 둘다 참이어야 참 printf("\nAdapter number out of range.\n"); pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); return -1; } for(d=alldevs, i=0; i< inum-1 ;d=d->next, i++); //사용자가 선택한 장치 목록을 선택 if((adhandle= pcap_open_live(d->name, 65536, 1, 1000, errbuf )) == NULL) { //실제 네트워크 디바이스 오픈 printf("\nUnable to open the adapter. %s is not supported by WinPcap\n", d->name); pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); return -1; } if (pcap_compile(adhandle, &fcode, packet_filter, 1, NULL) <0 ) { //패킷 필터링 정책을 위해 pcap_compile()함수 호출 //사용자가 정의한 필터링 룰을 bpf_program 구조체에 저장하여 특정 프로토콜 패킷만 수집 printf("\nUnable to compile the packet filter. Check the syntax.\n"); pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); return -1; } if (pcap_setfilter(adhandle, &fcode)<0) { //pcap_compile() 함수내용을 적용하기 위해 pcap_setfilter() 함수가 사용된다. printf("\nError setting the filter.\n"); pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); return -1; } printf("\nlistening on %s...\n", d->description); // 디바이스 정보 출력 pcap_freealldevs(alldevs); // 해제 while ((res = pcap_next_ex(adhandle, &header, &pkt_data)) >= 0) { if (res == 0) continue; print_ether_header(pkt_data); pkt_data += 14; print_arp_header(pkt_data); } return 0; } ///// 출력 void print_ether_header(const unsigned char *pkt_data) { // 이더넷 정보를 출력함 struct ether_header *eth; //이더넷 헤더 정보를 담을 수 있는 공간의 이더헤더의 구조체를 eth로 지정 eth = (struct ether_header *)pkt_data; // 구조체 eth에 패킷 정보를 저장 unsigned short eth_type; eth_type= ntohs(eth->ether_type); // 인자로 받은 값을 리틀 엔디안 형식으로 바꾸어줌 if (eth_type == 0x0806) {// ARP 패킷인 부분만 잡기! printf("\n====== ARP packet ======\n"); printf("\nSrc MAC : "); for (int i=0; i<=5; i++) printf("%02x ",eth->ethersed_mac.mac_add[i]); printf("\nDst MAC : "); for (int i=0; i<=5; i++) printf("%02x ",eth->etherdst_mac.mac_add[i]); printf("\n"); } } void print_arp_header(const unsigned char *pkt_data) { // ARP 패킷 정보를 출력 struct arp_header *arprqip; struct arp_header *arprpip; struct arp_header *arpmac; struct arp_header *arpop; arprqip = (struct arp_header *)pkt_data; arprpip = (struct arp_header *)pkt_data; arpmac = (struct arp_header *)pkt_data; arpop = (struct arp_header *)pkt_data; unsigned short Arpopcode = ntohs(arpop -> Op_code); // 인자로 받은 값을 리틀 엔디안 형식으로 바꾸어줌 if (Arpopcode == 0x0001) { // request = 1 printf(" ******* request ******* \n"); printf(" Sender IP : %s\n ", inet_ntoa(arprqip -> Arpsed_ip)); // 바이트 순서의 32비트 값을 주소값으로 변환하기 위함(in_addr 필요) printf("Target IP : %s\n ", inet_ntoa(arprqip -> Arptar_ip)); printf("\n"); } if (Arpopcode == 0x0002) { // reply = 2 printf(" ******** reply ******** \n"); printf(" Sender IP : %s\n ", inet_ntoa(arprpip -> Arpsed_ip)); printf("Sender MAC : "); for (int i=0; i <=5; i ++) printf("%02x ",arpmac -> Arpsed_mac.mac_add[i]); printf("\n"); printf(" Target IP : %s\n ", inet_ntoa(arprpip -> Arptar_ip)); printf("Target MAC : "); for (int i=0; i <=5; i ++) printf("%02x ",arpmac -> Arptar_mac.mac_add[i]); printf("\n"); } }* 실행 모습 *
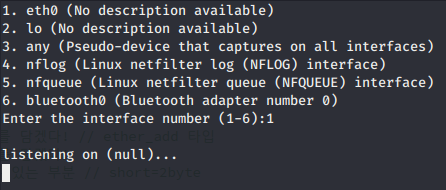
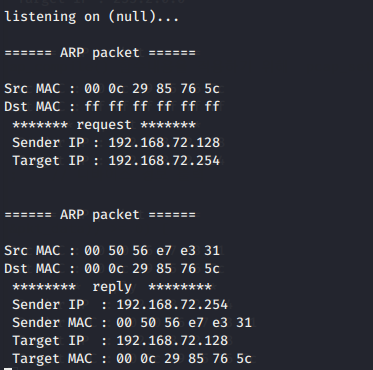
위 글은 공부 목적으로 개발된 것입니다!!
불법적인 행동에 쓰지 마세요!!!!!!
'Coding > 개발' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Snort] Rule 명령어 (0) 2020.06.05